Address: No. 199, Weiwu Road, Yueqing Economic Development Zone, Zhejiang Province, China.
Electrical sockets and plugs are essential elements of modern life, connecting our devices to power sources in a safe and efficient manner. Over time, these designs have evolved to meet the changing needs of industries and households alike. From basic single-phase plugs to complex, ruggedized industrial 3 phase plug systems, this evolution reflects both advancements in technology and responses to user demands for functionality, safety, and reliability.
The Early Days of Electrical Plugs and Sockets
The concept of electrical plugs and sockets emerged in the late 19th century as electricity began to be adopted for commercial and residential use. Early designs were simple and often lacked the safety measures we now take for granted. As more devices came into use, the need for standardized connections became clear. Early sockets and plugs were largely ungrounded, which limited their safety and suitability for many applications. As a result, designs soon incorporated grounding features, improving safety by preventing electric shocks from short circuits or faults.
The Shift to Industrial-Grade Designs
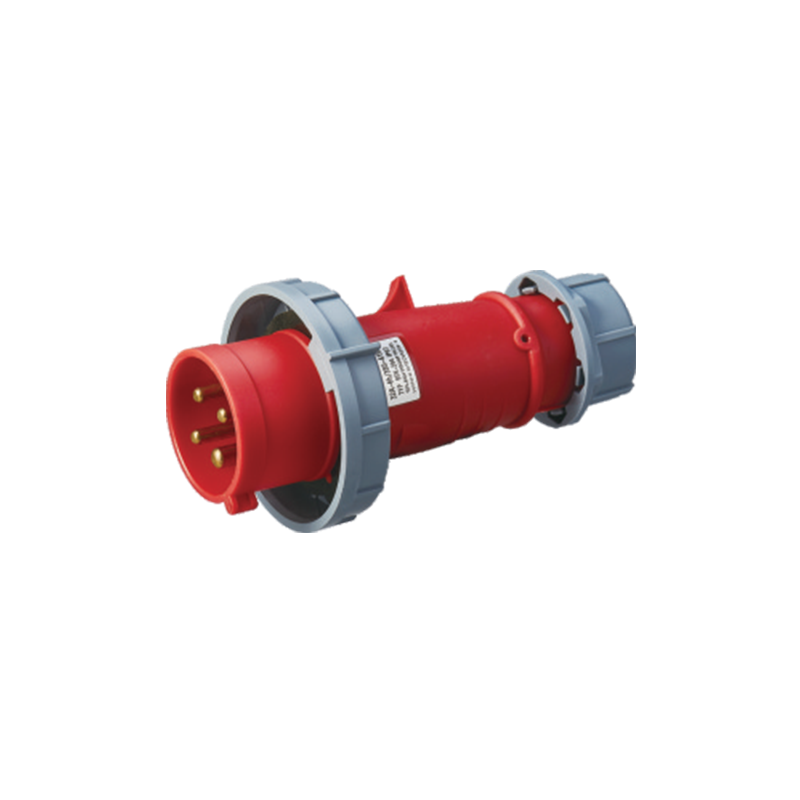
As industries grew in scale and complexity, so too did their power needs. Equipment required higher currents, necessitating designs that could handle greater electrical loads safely. This led to the development of robust industrial sockets and plugs designed specifically for heavy-duty environments. Among these innovations was the industrial 3 phase plug. Unlike single-phase plugs, which provide power through one live wire, a neutral, and a ground, three-phase plugs supply power through three live wires, allowing for a more stable and efficient power supply. This setup is ideal for machinery that requires a steady, high-power output.
Industrial plugs are typically made of durable materials to withstand harsh environments. Unlike their domestic counterparts, they often have reinforced housings, weather-resistant coatings, and secure locking mechanisms to ensure stable connections even under challenging conditions. The introduction of double industrial sockets also became common in many facilities, as they allow multiple machines or devices to connect to the same power source, increasing operational efficiency without compromising safety.
Innovations in Safety and Design
With electricity playing a critical role in both homes and workplaces, safety has become paramount in plug and socket design. Over the years, regulations and standards have been implemented globally to ensure products meet specific safety requirements. For instance, modern plug and socket designs often incorporate safety shutters that prevent accidental contact with live components. Materials used for industrial plugs and sockets are also typically flame-retardant and resistant to chemicals, which is crucial for applications in areas with hazardous materials or bad temperatures.
The plug and socket box is another advancement that has greatly improved safety in industrial settings. These boxes provide a protective enclosure for sockets and plugs, shielding them from dust, moisture, and other environmental factors. In some cases, these boxes are equipped with lockable covers, adding another layer of security to prevent unauthorized access or accidental disconnections. This feature is particularly valuable in manufacturing, construction, and other industries where reliable power connections are essential for productivity and safety.
The Impact of Global Standardization
A major factor in the evolution of plugs and sockets has been the push for global standardization. Historically, different countries developed their own plug and socket types, creating challenges for international industries and travelers alike. In recent years, organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have worked to establish standards that promote compatibility and safety worldwide. For example, the IEC 60309 standard provides specifications for industrial plugs and sockets, ensuring that products made according to this standard can be used safely and consistently across different regions.
Standardized designs such as the industrial 3 phase plug allow manufacturers to produce equipment that is compatible with international systems. These plugs, which often have color-coded indicators to denote their voltage and current ratings, are widely recognized and trusted by industries globally. Standardization has also encouraged innovation in double industrial sockets, making it easier to adopt new technologies while maintaining compatibility with existing systems.
Future Trends in Plug and Socket Design
The future of plug and socket design is poised to focus on smart technologies and increased environmental sustainability. As industries move towards automation and the use of smart devices, the need for smarter plug-and-socket systems has grown. Some manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate sensors and IoT capabilities into sockets, allowing them to monitor usage, detect faults, and communicate data to central systems for predictive maintenance. This shift towards “smart” electrical systems could revolutionize power distribution in both residential and industrial settings, creating more efficient and reliable infrastructures.
Another anticipated trend is the use of eco-friendly materials and designs. Manufacturers are exploring recyclable or biodegradable materials to reduce waste associated with discarded electrical components. This shift aligns with global sustainability goals and could advance to more widespread adoption of green manufacturing practices within the plug and socket industry.